E-Commerce
E-COMMERCE
What is E-commerce ?
Ecommerce or electronic commerce is the trading of goods and services on the internet . It is your bustling city center or brick-and-mortar shop translated into zeroes and ones on the internet superhighway . This year , an estimated 2.14 billion people word wide will buy goods and services online , and the number of Prime members shopping amazon stores now tops 150 million .
It is commonly known as electronic marketing . It consist of buying and selling goods and services over an electronic system such as the internet .E-commerce is the purchasing , selling &exchanging goods and services over computer network or internet through which transactions or terms of sale are performed electronically .
Why E-commerce ?
Here are a few important benefits , among a host of others, of this revolutionary model of business:
- E-commerce bridges the gap between local sellers and global audiences , thereby helping them in widening their reach across the global market segments .
- The consumers are provided with a gamut of options for procurements .
- It facilitates the round-the-clock conduct of trade .
The following are the different types of E-commerce platforms :-
- Business-to-Business (B2B)
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
- Consumer-to-Business (C2B)
- Business-to-Administration (B2A)
- Consumer-to-administration (C2A)

A B2B model of business involves the conduct of trade between two or more businesses / companies . the channels of such trade generally include conventional wholesalers and producers who are dealing with retailers .
Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
Business-to-Consumer model of business deals with the retail aspects of E-commerce , i.e. the sale of goods and / or services to the end consumer through digital means . The facility , which has taken the business world by storm , enables the consumer to have a detailed look at their proposed procurements before placing an order . After the placement of such orders , the company / agent receiving the order will then deliver the same to the consumer in a consumer time-span . Some of the business operating in this channel include well-known players like Amazon , Flipkart , etc.
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
This business model is leveraged by a consumer for selling used goods and/or services to other consumers through the digital medium. The transactions here are pursued through a platform provided by a third party, the likes of which include OLX, Quickr, etc.
Consumer-to-Business (C2B)
A C2B model is the exact reversal of a B2c model. While the latter is serviced to the consumer by a business, the C2B model provides the end consumers with an opportunity to sell their products/services to companies. The method is popular in crowdsourcing based projects, the nature of which typically includes logo designing, sale of royalty-free photographs/media/design elements, and so on and so forth.
Business-to-Administration (B2A)
This model enables online dealings between companies and public administration, i.e. the Government by enabling the exchange of information through central websites. It provides businesses with a platform to bid on government opportunities such as auctions, tenders, application submission, etc. The scope of this model is now enhanced, thanks to the investments made towards e-government
Consumer-to-administration (C2A)
The C2A platform is meant for consumers, who may use it for requesting information posting feedbacks concerning public sectors directly to the government authorities/administration. Its areas of applicability include:
- The dissemination of information.
- Distance learning.
- Filing of tax returns.
- Seeking appointments, information about illness, payment of health services, etc.
- Shopify.
- Wix.
- BigCommerce
- adobe Commerce
- wooCommerce
- Prestashop
- squarespace
- Big cartel
- weebly.
- 3dcart
- Volusion
- Opencart
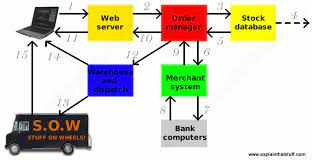
- Sitting at her computer, a customer tries to order a book online. her Web browser communicates back-and-fourth over the Internet.
- The Web server sends her order to the order manager.
- The order manager queries a database to find out whether what the customer wants is actually in stock.
- The bank computer confirms whether the customer has enough funds.
- The merchant system might make extra checks with the customer's own bank computer.
- The goods are delivered to the customer.
- The order manager sends a request to the warehouse to dispatch the goods to the customer.







Comments
Post a Comment